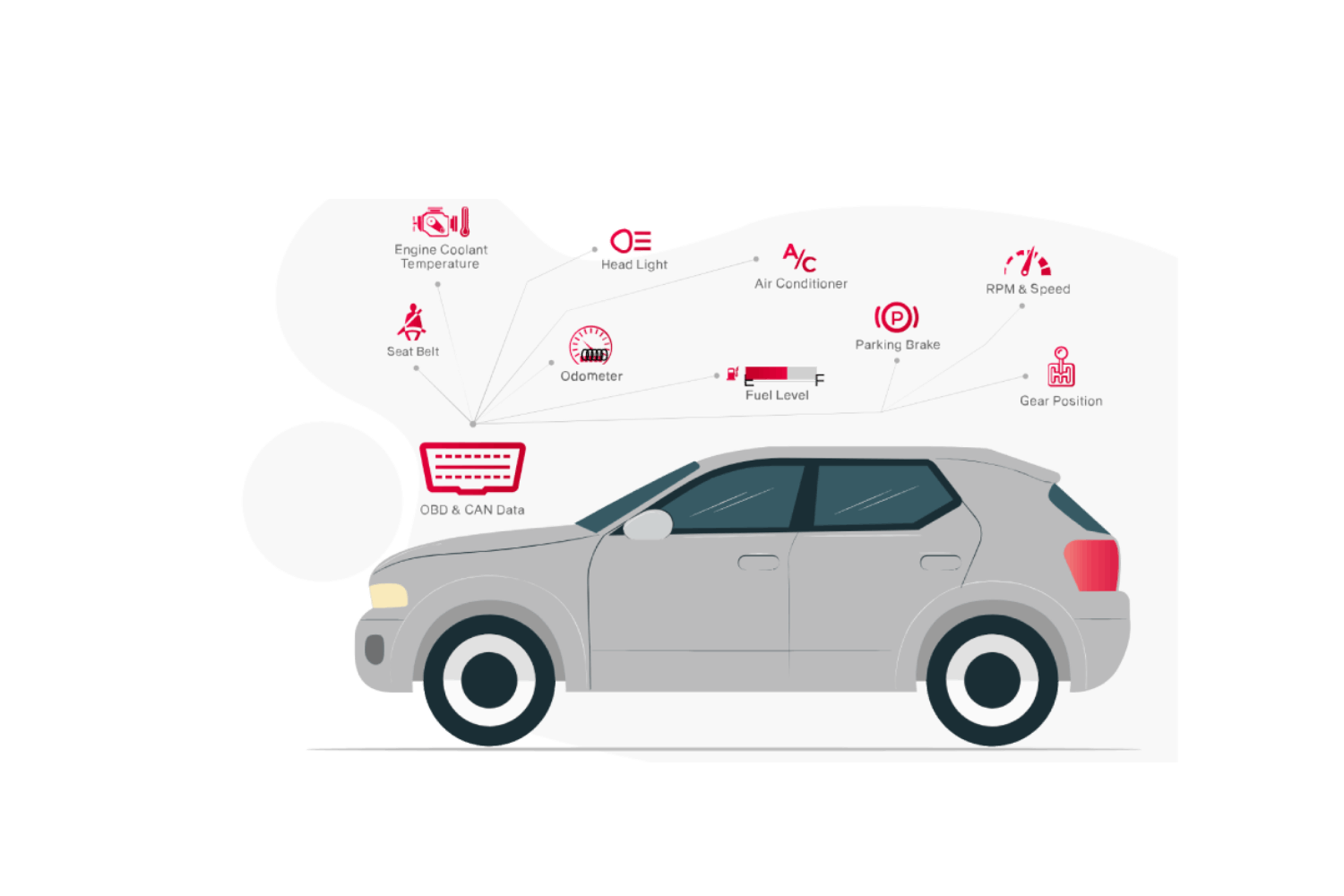
OBD - Can Tracker
OBD-II and CAN Integration:
In modern vehicles, the OBD-II system uses the CAN protocol as the communication backbone to gather diagnostic information from various ECUs and sensors. This integration enables standardized access to vehicle data, making it easier for technicians and diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s computer system.
Using the OBD-II port, which is typically located under the dashboard, diagnostic tools or scanners can establish a connection to the vehicle’s CAN bus. They can then retrieve diagnostic trouble codes, read live sensor data, and perform various diagnostic functions. This allows for efficient troubleshooting, maintenance, and repair procedures.
1.Calculated engine load
2.Engine coolant temperature
3.Engine RPM
4.Vehicle speed
5. Vehicle Odometer
6. Intake manifold absolute pressure
7. MAF air flow rate
8. Distance travelled with malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on
9. Warm-ups since codes cleared
10. Distance travelled since codes cleared
11. Run time since engine start
12. Throttle position
13. Fuel Input Level
14. Engine oil temperature
15. Fuel Type
16. State of charge (SOC)
17. Distance to empty (DTE)
18. Door status
19. Door status
20. Ac Status
21. Ac blower speed
22. Head light status
23. Brake light status
24. Indicator/Hazard light status
25. Driver seat belt status
26. Passenger seat belt status
27. Gear position
28. Charging mode
29. Charging time

